Fed
The U.S. Federal Reserve hiked its benchmark interest rate by 75 basis points (bps) for the fourth consecutive time, as inflation has remained stubbornly high.
This move, which brings the federal funds rate to a range of 3.75% to 4%, comes after a stronger-than-expected Consumer Price Index (CPI) report for September. The latest numbers showed no signs that inflation has peaked. Led by rent and owners' equivalent rent, inflation for services notably accelerated month over month. Coupled with strong employment data, persistent inflation has left the Fed with little choice but to press on.
On Wednesday, the Fed hinted it may soon consider slowing the pace of its rate increases, noting that it would “take into account the cumulative tightening of monetary policy, the lags with which monetary policy affects economic activity and inflation, and economic and financial developments” when considering future actions. However, Fed Chair Jerome Powell reiterated that the central bank would “stay the course until the job is done” and said it is “very premature” to talk about pausing rate increases.
“Incoming data since our last meeting suggests that the ultimate level of interest rates will be higher than previously expected,” Powell said. “The question of when to moderate the pace of increases is now much less important than the question of how high to raise rates and how long to keep monetary policy restrictive, which will be our principal focus.”
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rallied immediately following the Fed’s announcement, with its yield briefly falling below 4%. However, it rose to 4.09% at market close after Powell answered questions from the press. Bond yields move inversely to prices. The S&P 500 closed down 2.5% on Wednesday.
Here are reactions from economists Jared Franz and Darrell Spence and fixed income portfolio managers Pramod Atluri and Damien McCann on the Fed’s latest hike, the state of the U.S. economy and positioning fixed income portfolios in this environment.
Market may be underestimating how high rates will ultimately go
Jared Franz and Darrell Spence, economists
The market has made progress in raising its expectations for the peak fed funds rate, but still may not be fully prepared for how far the Fed needs to go, nor the likely economic impact of doing so. It’s worth remembering the fed funds rate was 5% to 6% for much of the mid-1990s when inflation was much lower than it is now; most historical tightening cycles have not ended until the fed funds rate was solidly higher than inflation. Heightened rate expectations in recent months have already caused a sharp increase in bond yields and a resumption of the decline in equity prices, but we could still have further to go.
Inflation may also remain stubbornly higher than the market and the Fed anticipate. Weakness in the housing sector and other areas suggests price pressures should be easing, but inflation reports for the past few months have surprised to the upside. There appear to be numerous longer-term drivers of structural inflation that could persevere, including elevated inflation expectations, the lingering impact of household savings accrued during the pandemic, the climate transition, geopolitical risk and companies bringing supply chains closer to home. It is a realistic scenario that inflation could remain above the Fed's target of 2% for an extended period. In the extreme, inflation could persist at 5% structurally.
There’s a high bar to clear for the Fed to fully stop quantitative tightening. It will likely cease only in the event of extreme market turmoil. A recession is not likely to trigger the Fed to stop shrinking its balance sheet, although it could slow the pace. Some Fed governors want to get out of the quantitative easing business altogether. Doing so would neutralize an important criticism that the central bank is exerting undue influence on markets by holding so many fixed income securities as well as overstimulating the housing sector through its holdings of $2.6 trillion in mortgage-backed securities.
Rate hike expectations have risen substantially
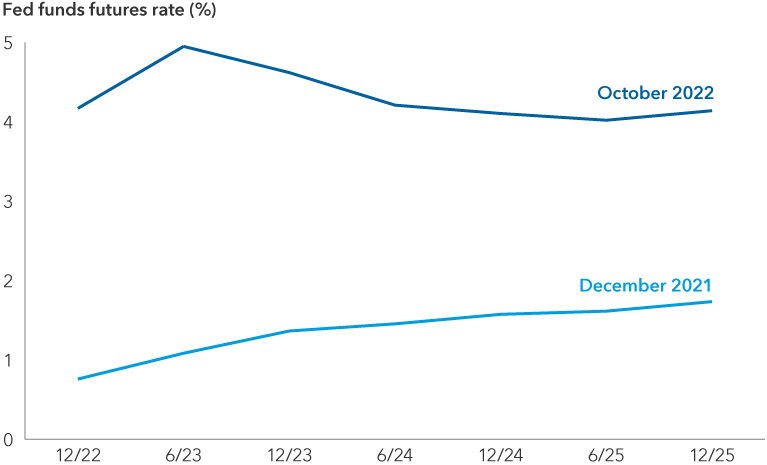
Source: Capital Group, FactSet.
Lackluster earnings could continue to drag equities down
Darrell Spence, economist
Historically, bear markets associated with a recession have had a median decline of 35% and a median duration of 17 months. If there is a recession in the U.S., stocks could have further to fall and the slump could persist well into 2023.
We have seen the valuation contraction part of the bear market, but not the part associated with a decline in earnings. Economists’ earnings-per-share (EPS) projections have come down in recent months, but consensus estimates for 2023 EPS growth are still around 6%, which seems too optimistic to me.
In prior recessions, it has been normal for corporate earnings to fall by 15% to 20%. Given slowing economies around the world, a strong U.S. dollar and margin pressures from rising labor costs, it is not a stretch to think that we could see another leg down in equities. If EPS dropped 15%, the S&P 500 would need to trade at nearly 20 times price to earnings to maintain its current level, which does not strike me as cheap in an environment where 10-year bond yields are around 4% (and perhaps heading to 5%).
On average, the S&P 500 Index has tended to peak seven months before the economic cycle has peaked (as measured by industrial production). Following a peak in production, the market has tended to fall for another four to six months, and then has started to rise in advance of the turn in economic activity and corporate earnings. We have yet to see a peak in production. A further decline in equity prices would be consistent with how the market and economy have interacted in past bear markets.
Core bonds: shifting to the front end of the yield curve
Pramod Atluri, core bond portfolio manager
The yield curve has inverted as the market prices in the Fed’s increasing short-term rates to fight inflation and a rising chance of a recession. With yields now reflecting a fed funds rate of 5% by mid-2023, I think there is compelling value at the front end of the curve; thus, we have moved our core bond portfolios from holding less shorter-term Treasuries than their benchmark to holding more. The overall duration of the portfolios is still neutral as the near-term outlook for inflation remains uncertain.
Many real-time and forward-looking indicators show signs that Fed rate hikes have had a dampening impact on the economy. An increasing number of voices are suggesting the Fed should slow and ultimately pause rate hikes in 2023 in the 4.5% to 5% range to assess the impact of its actions before potentially hiking further. But ultimately, the next few inflation reports will determine if Fed officials have the luxury of doing this. I think an extended pause at around 5% would be reasonable given what we know today, which implies interest rates may only drift modestly higher from current levels. The risk to this view is if inflation continues to grow more quickly than expected in the months ahead.
When the Fed pauses its hiking cycle, I think we are likely to see shorter-term Treasuries rally and longer-term bonds lag, which would lead the yield curve to quickly pivot from being inverted (where short-term yields are higher than long-term) to positively sloped (where long-term yields are higher than short-term). This potential yield curve steepening could be quite significant. Given the prospective opportunity and the difficulty predicting when this transition will occur, I would rather be a little early than late.
Economic resilience buoys credit assets
Damien McCann, credit portfolio manager
The continued resilience of the consumer is supportive of credit assets. This is due, in large part, to low unemployment and bank account balances that still show some benefits from COVID-era stimulus. Investment-grade (rated BBB/Baa and above) credit spreads could widen from current levels as the economy weakens. Corporate balance sheets are currently in decent shape and can likely withstand some bumps in the road before they become overly stressed. Aggregate leverage in the credit universe is not high. I expect deterioration in corporate fundamentals to be a function of the severity of the economic downturn. My base case is we won’t experience a severe recession (a more moderate recession seems more likely to me). The banking system is also well capitalized.
In multisector credit portfolios, I see select investment opportunities in securitized credit and some areas of emerging markets (EM) debt. Some EM issuers that our analysts believe to be resilient look appealing as broad-based weakness in the sector has pushed their spreads wider than may be warranted.
I remain cautious on high yield, even though yields have risen substantially, fundamentals have improved, and default rates remain low by historical standards. High yield has typically not done well in monetary tightening cycles. Therefore, I prefer to be patient and wait for a more attractive entry point.
 Darrell Spence
Darrell Spence
 Jared Franz
Jared Franz
 Pramod Atluri
Pramod Atluri
 Damien McCann
Damien McCann